Base Investments: A Comprehensive Guide
Base Investments: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In the realm of finance, base investments play a pivotal role in building a diversified and stable portfolio. These investments provide a foundation of stability and growth, offering investors a haven during market fluctuations. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of base investments, exploring their types, benefits, and strategies for successful implementation.
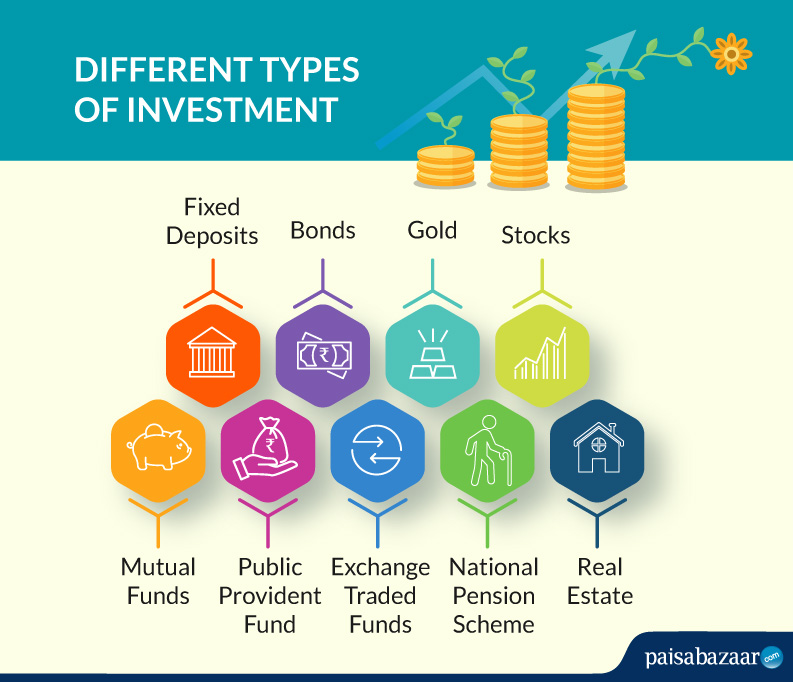
Types of Base Investments
Base investments encompass a wide range of asset classes, each with its unique characteristics and risk-reward profile. The most common types include:
- Bonds: Bonds are fixed-income securities that represent a loan to a government or corporation. They pay regular interest payments and repay the principal amount at maturity.
- Cash Equivalents: Cash equivalents are short-term, highly liquid investments that are similar to cash. Examples include money market accounts and certificates of deposit (CDs).
- Real Estate: Real estate investments involve purchasing property, either residential or commercial, with the goal of generating rental income or capital appreciation.
- Commodities: Commodities are physical assets, such as gold, silver, or oil, that are traded on exchanges. They provide diversification and potential inflation protection.
- Preferred Stocks: Preferred stocks are hybrid securities that combine features of bonds and stocks. They pay fixed dividends and have a higher claim on assets than common stocks.
Benefits of Base Investments
Base investments offer numerous benefits to investors, including:
- Stability: Base investments tend to be less volatile than other asset classes, providing a cushion during market downturns.
- Income Generation: Bonds and preferred stocks provide regular income payments, offering a steady stream of cash flow.
- Diversification: By incorporating base investments into a portfolio, investors can reduce overall risk by spreading their investments across different asset classes.
- Inflation Protection: Commodities and real estate can provide some protection against inflation, as their value tends to increase with rising prices.
- Tax Advantages: Certain base investments, such as municipal bonds, offer tax-free income, which can enhance returns.
Strategies for Successful Base Investments
To maximize the benefits of base investments, investors should consider the following strategies:
- Diversify: Allocate investments across different base asset classes to reduce risk and enhance returns.
- Consider Risk Tolerance: Base investments should align with an investor’s risk tolerance and financial goals.
- Research: Conduct thorough research on potential investments to assess their risk and return potential.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging: Invest a fixed amount of money at regular intervals to smooth out market fluctuations.
- Rebalance Regularly: Periodically adjust the portfolio to maintain the desired asset allocation and risk level.
Common Pitfalls
While base investments can be valuable additions to a portfolio, there are some common pitfalls to avoid:
- Overconcentration: Investing too heavily in a single base asset class can increase risk.
- Timing the Market: Attempting to time the market for entry and exit points can lead to missed opportunities and losses.
- Chasing Returns: Investing in base investments solely for high returns can lead to excessive risk-taking.
- Ignoring Risk: Failing to properly assess the risks associated with base investments can result in significant losses.
- Neglecting Rebalancing: Allowing the portfolio to drift from its target asset allocation can increase risk and reduce returns.
Conclusion
Base investments form the cornerstone of a well-diversified and stable portfolio. By understanding the different types of base investments, their benefits, and effective strategies, investors can harness their potential for growth and income generation while mitigating risk. However, it is crucial to approach base investments with a prudent mindset, avoiding common pitfalls and seeking professional advice when necessary. By carefully considering the principles outlined in this guide, investors can make informed decisions and build a solid financial foundation for the future.
FAQs about Base Investments
What is a base investment?
A base investment is a type of investment that is designed to provide a stable and predictable return. Base investments typically have a low risk profile and are often used as a way to preserve capital.
What are some examples of base investments?
Some examples of base investments include:
- Certificates of deposit (CDs)
- Money market accounts
- Treasury bills
- Corporate bonds
- Real estate
How do base investments work?
Base investments work by providing investors with a fixed rate of return. This rate of return is typically set at a level that is higher than the current inflation rate. As a result, base investments can help investors to protect their purchasing power over time.
What are the benefits of investing in base investments?
There are a number of benefits to investing in base investments, including:
- Stability: Base investments are designed to provide a stable and predictable return. This can be beneficial for investors who are looking for a way to preserve their capital.
- Low risk: Base investments typically have a low risk profile. This makes them a good option for investors who are not comfortable with taking on a lot of risk.
- Tax benefits: Some base investments, such as CDs and Treasury bills, are tax-free. This can help investors to reduce their tax liability.
What are the risks of investing in base investments?
There are a few risks associated with investing in base investments, including:
- Inflation risk: Base investments are not immune to inflation. If the inflation rate rises, the value of your investment may decline.
- Interest rate risk: Base investments are also subject to interest rate risk. If interest rates rise, the value of your investment may decline.
- Default risk: If the issuer of a base investment defaults, you may lose your investment.
How do I choose the right base investment?
When choosing a base investment, it is important to consider your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. You should also consider the specific features of each investment, such as the interest rate, maturity date, and tax implications.
Conclusion
Base investments can be a good way to preserve capital and generate a stable income. However, it is important to understand the risks involved before investing in any base investment.
Also read: Perawatan Burung Murai Batu